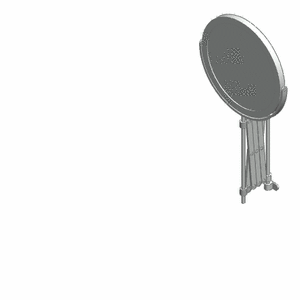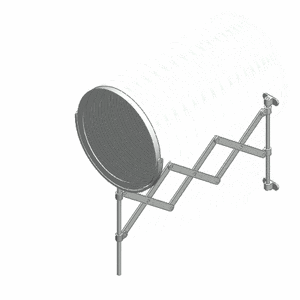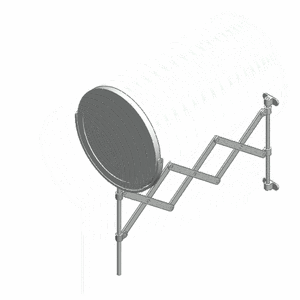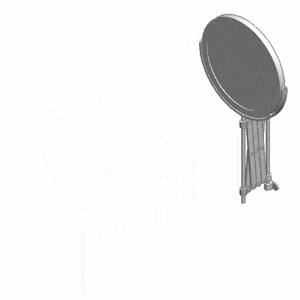Scissor linkages: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Techniques infobox | {{Techniques infobox | ||
|image = Pantograph Mirror.gif | |image = Pantograph Mirror.gif | ||
| | |designers = Phil Jergenson | ||
|date = | |date = | ||
|vitamins = | |vitamins = | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
|tools = [[Wrenches]] | |tools = [[Wrenches]] | ||
|git = | |git = | ||
| | |files = | ||
|suppliers = | |||
|reversible = true | |||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
A pantograph (Greek roots παντ- "all, every" and γραφ- "to write", from their original use for copying writing) is a [[Linkage (mechanical)|mechanical linkage]] connected in a manner based on parallelograms so that the movement of one pen, in tracing an image, produces identical movements in a second pen. If a line drawing is traced by the first point, an identical, enlarged, or miniaturized copy will be drawn by a pen fixed to the other. Using the same principle, different kinds of pantographs are used for other forms of duplication in areas such as sculpture, minting, engraving, and milling. | |||
Because of the shape of the original device, a pantograph also refers to a kind of structure that can compress or extend like an [[accordion]], forming a characteristic [[rhomboidal]] pattern. This can be found in extension arms for wall-mounted mirrors, temporary fences, [[pantographic knife|pantographic knives]], [[scissor lift]]s, and other [[scissor mechanism]]s such as the [[Pantograph (rail)|pantograph]] used on electric locomotives and trams. | |||
=Challenges= | =Challenges= | ||
=Approaches= | =Approaches= | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
1920px-Pantograph in action.svg.png| | 1920px-Pantograph in action.svg.png| | ||
| Line 28: | Line 32: | ||
Pantograph etching mechanism.jpg| | Pantograph etching mechanism.jpg| | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pantograph Pantograph] | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pantograph Wikipedia: Pantograph] | ||
* [https://archive.org/details/1800-mechanical-movements-devices-and-appliances_202005/ 1800 Mechanical movements, devices, and appliances] | * [https://archive.org/details/1800-mechanical-movements-devices-and-appliances_202005/ 1800 Mechanical movements, devices, and appliances] | ||
* [http://507movements.com/ 507 Mechanical Movements] | * [http://507movements.com/ 507 Mechanical Movements] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:04, 25 September 2021
| Reusability | Reversible |
|---|---|
| Designers: | Phil Jergenson |
| Tools: | Wrenches |
| Parts: | Frames, Bolts, Nuts, End caps |
| Techniques: | Bolting |
Introduction
A pantograph (Greek roots παντ- "all, every" and γραφ- "to write", from their original use for copying writing) is a mechanical linkage connected in a manner based on parallelograms so that the movement of one pen, in tracing an image, produces identical movements in a second pen. If a line drawing is traced by the first point, an identical, enlarged, or miniaturized copy will be drawn by a pen fixed to the other. Using the same principle, different kinds of pantographs are used for other forms of duplication in areas such as sculpture, minting, engraving, and milling.
Because of the shape of the original device, a pantograph also refers to a kind of structure that can compress or extend like an accordion, forming a characteristic rhomboidal pattern. This can be found in extension arms for wall-mounted mirrors, temporary fences, pantographic knives, scissor lifts, and other scissor mechanisms such as the pantograph used on electric locomotives and trams.