3D printers: Difference between revisions
From
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
=Approaches= | =Approaches= | ||
Use [https://wiki.replimat.org/wiki/Bearings#Linear_Bearings linear bearings], [[motors]], and a [[controller]] to build a 3D printer. A hotend designed to consume plastic pellets instead of filament allows for direct recycling of shredded plastic goods. | Use [https://wiki.replimat.org/wiki/Bearings#Linear_Bearings linear bearings], [[motors]], and a [[controller]] to build a 3D printer. A hotend designed to consume plastic pellets instead of filament allows for direct recycling of shredded plastic goods. | ||
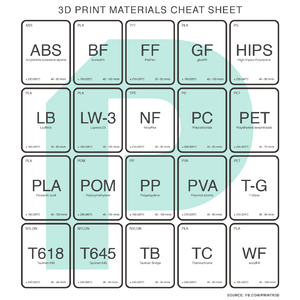
[https://www.appropedia.org/Polymer_recycling_codes_for_distributed_manufacturing_with_3-D_printers Polymer recycling codes for distributed manufacturing with 3-D printers] | |||
=Tools= | =Tools= | ||
Revision as of 04:12, 13 September 2020
Challenges
Subtractive manufacturing can produce many goods - particularly with multi-step production processes and multiple parts. But some objects can't be made that way. Others are simpler and faster to manufacture in a single operation additively.
Approaches
Use linear bearings, motors, and a controller to build a 3D printer. A hotend designed to consume plastic pellets instead of filament allows for direct recycling of shredded plastic goods.
Polymer recycling codes for distributed manufacturing with 3-D printers
Tools
Parts
| Quantity | Part | Link |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mahor pellet hot end | mahor.xyz |
Workflows
- All in one 3D printer test print
- Smart compact temperature calibration tower
- PETG Basics
- PETG Hints, safety, and techniques