Drying racks
| Tools: | Wrenches |
|---|---|
| Parts: | Pallets, Harvest hangers, Frames, Nuts, Bolts, End caps |
| Techniques: | Shelf joints, Tri joints |
Introduction
Drying is a mass transfer process consisting of the removal of water or another solvent by evaporation from a solid, semi-solid or liquid. This process is often used as a final production step before selling or packaging products. To be considered "dried", the final product must be solid, in the form of a continuous sheet (e.g., paper), long pieces (e.g., wood), particles (e.g., cereal grains or corn flakes) or powder (e.g., sand, salt, washing powder, milk powder). A source of heat and an agent to remove the vapor produced by the process are often involved. In bioproducts like food, grains, and pharmaceuticals like vaccines, the solvent to be removed is almost invariably water. Desiccation may be synonymous with drying or considered an extreme form of drying.
Challenges
Racks for the purposes of drying must allow sufficient airflow and make efficient use of 3 dimensional space through modularity and stacking.
Approaches
-
Ken Isaacs pallet
-
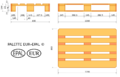
EUR pallet
-
Pallet
Building off from pallets allows for drying racks to be easily moved by loading equipment, stacked, and stored or shipped using all the other projects designed to interoperate with pallets.